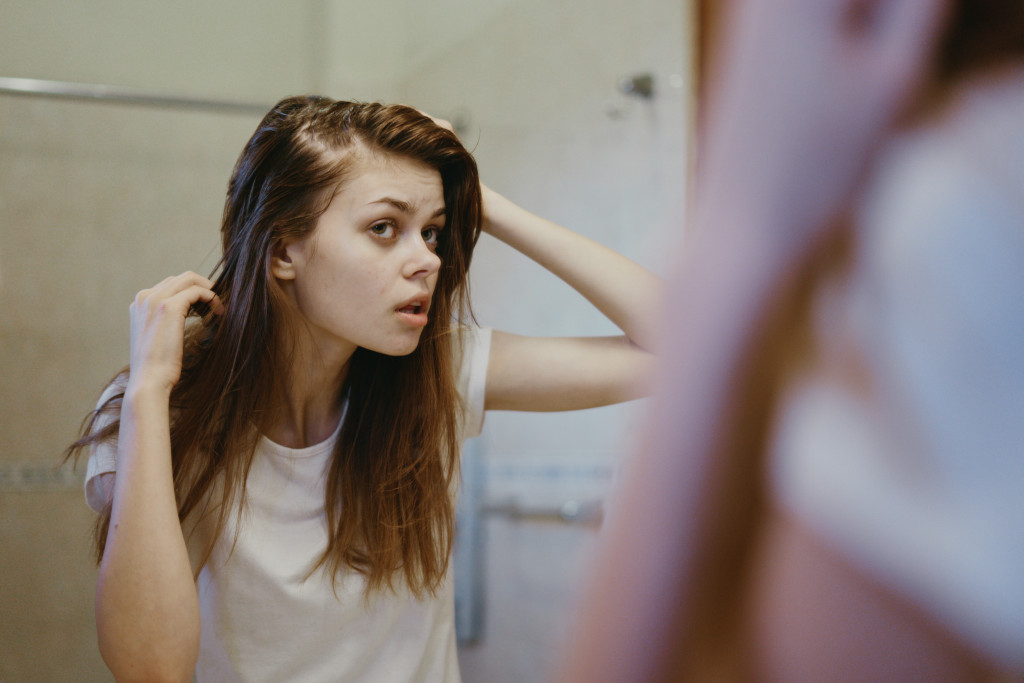
Alopecia areata is an immune system disorder that causes balding, frequently in small patches on the head or other parts of the body. It is a common condition that affects at least two percent of the population. According to the National Alopecia Areata Foundation, it is believed to affect men and women equally. But as of yet, the exact cause or causes are unknown.
It can be stressful and emotionally challenging to live with alopecia areata, but there are ways to manage the condition and live your best life. Here’s a look at how you can take control of your health and well-being with alopecia areata.
Educate Yourself About Alopecia Areata
The more you know about alopecia areata, the better prepared you will be to face any challenges that come along with it. Read up on the latest research and treatments available for alopecia areata, so you can make informed decisions about your health care. There is also a wealth of resources available online from support groups and forums that can help provide emotional support for those living with alopecia areata.
What is alopecia areata?
Alopecia areata is a type of hair loss that affects up to 6.8 million people in the United States. It is an autoimmune disorder caused when your immune system mistakenly attacks your own hair follicles, causing them to become weak and eventually stop producing hair.
Although alopecia areata can have devastating effects, understanding the condition can help people manage or even prevent it from happening in the first place.
What causes alopecia areata?
Alopecia areata is a mystery to science as its exact cause is still unknown. However, it is believed to be an autoimmune disorder triggered by environmental factors such as stress, diet, and genetics. People who suffer from chronic illnesses such as asthma or diabetes may be more likely to develop alopecia areata due to their weakened immune systems.
Also, people with a family history of alopecia areata may be more prone to developing the condition. This is the most common cause of alopecia areata.
Symptoms of alopecia areata
The most common symptom of alopecia areata is patchy baldness on the scalp or other areas of the body. This can range from a few patches of missing hair to complete baldness across the entire scalp or body. Other symptoms include itching and burning sensations around the affected area and, in some cases, brittle nails and darkening of the skin surrounding the affected region.
Moreover, people with alopecia areata may also experience depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem due to their appearance. In fact, studies have shown that people with alopecia areata have higher rates of depression and anxiety than the general population.
Find Ways to Feel Good About Yourself

It’s normal to feel down or have negative thoughts when dealing with alopecia areata. But it’s important to remember that you’re still beautiful and worthy of love even if you don’t have a full head of hair.
Find activities that make you feel good about yourself, such as spending time outdoors or engaging in hobbies like painting or photography. Exercise can also be beneficial; not only does it help boost your mood, but it can also reduce stress levels which in turn can reduce flare-ups of the condition.
In addition, opting for alternative hair solutions, such as customized cranial prosthetics, can help you regain your confidence. Cranial prosthetics are lightweight caps that fit securely over the scalp and provide a natural-looking hairline to cover up any bald patches caused by alopecia areata. Investing in a cranial prosthetic can be an empowering experience and is worth considering if you’re looking for ways to feel better about yourself.
Seek Medical Treatment When Needed
When needed, seek medical treatment for any symptoms related to alopecia areata, such as itching or inflammation. There may also be treatments available such as:
- Topical solutions: Corticosteroid creams can be applied directly to the affected area to reduce inflammation and prevent further hair loss.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections can also be administered directly into bald patches in order to promote hair growth.
- Light therapy: Ultraviolet light treatments are sometimes used to stimulate the regrowth of lost hair.
- Medication: Certain medications, such as minoxidil, can be prescribed to help stimulate hair regrowth.
If these treatments aren’t working for you, talk to your doctor about other options, such as wigs or hairpieces, which may help hide any patchy areas caused by alopecia areata while giving you back some confidence in your appearance.
The Bottom Line
Living with alopecia areata doesn’t have to mean living a life of fear and frustration. By educating yourself about the condition, finding ways to love yourself, and seeking medical treatment if necessary, you can take control of your health and well-being and live your best life.