The growing human population has inevitably worsened the ecological disruption. It’s logical to say that a rise in world population has led to additional pressure on natural resources. After all, more people means high demand for water, energy, food, housing, and transportation. Moreover, it has put significant pressure on industrial companies to manufacture various goods to meet the growing demand.
Today, business leaders are exerting efforts to address the worsening ecological impact of human activity. Companies are integrating environmental and social concerns in their business interactions and operations to reduce their impact on the planet. For example, many corporate businesses rely on an IT company to support their tech needs in a smart, safe and productive way. Meanwhile, others support tech manufacturers that use recyclable materials in manufacturing devices and office equipment.
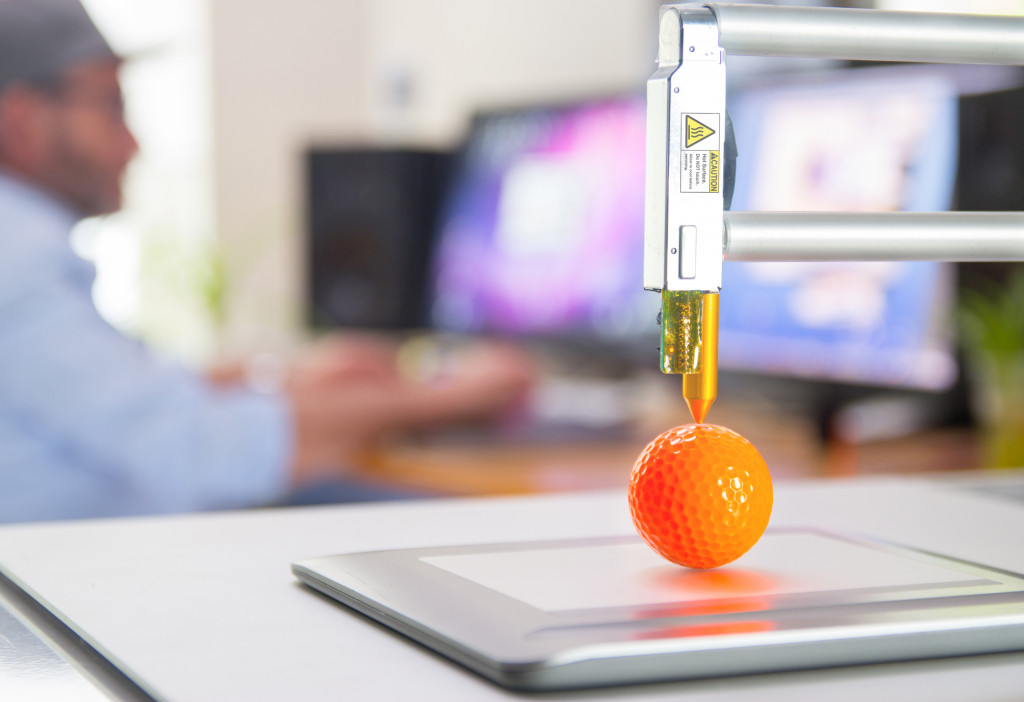
While eco-friendly technology has proven its capabilities in reducing its environmental impact, the industrial sector has discovered a recent innovation that enables smart and sustainable manufacturing. 3-D printing is now heralded as the key technology to transform the sustainability and environmental credentials of manufacturing. Also known as additive manufacturing, 3-D printing act as a viable alternative to traditional manufacturing processes. To know more about this emerging technology, we’ll talk about how 3-D printing can help manufacturing companies to become fully sustainable.
Efficient design
With 3-D printing, engineers can explore modern design methods, such as topology optimization, using more efficient and lightweight parts. Topology optimization software uses a computational algorithm for preexisting designs to optimize their weight and shape.
Meanwhile, in manufacturing systems that affect energy consumption, 3-D printing help produce lighter optimized components that lead to long-term benefits in fuel economy. In other words, every weight reduced from a vehicle’s weight means no fuel burned and no carbon dioxide emitted. Weight reductions, even in relatively smart portions, can result in greater savings and energy efficiency.
Besides topology optimization, manufacturers can also enhance product designs consisting of multiple components by 3-D printing. This approach is called part consolidation by manufacturing a product as a single unit instead of containing several parts.
Parts consolidation helps in reducing the number of components to be designed, reducing time, material, and labor. It also generates better-performing parts with increased durability because of tighter tolerances, fewer seams, fewer vibrations, and fewer areas for leaks.

Reduced emission and waste production
Traditional manufacturing methods are undoubtedly wasteful by consuming large amounts of raw materials and energy. Instead of creating the item from large pieces of plastic and metal, 3-D printing produces the item by layer. This practice will reduce the production of scrap waste by 70 to 90 percent compared to other traditional manufacturing systems, such as injection molding or CDC manufacturing.
In 3-D printing, most of the design process takes place on computers, which can be further improved with computer simulations. The process itself makes it possible to determine potential failures, so less waste and fewer prototypes will be generated.
3-D printing also streamlines the manufacturing process, resulting in fewer parts and efficiency gains. A great example is 3-D-printed electronics that combine mechanical and electrical functionalities to reduce the number of parts used. As a result, this allows engineers to focus on performance and durability.
Lesser carbon dioxide emissions are also achievable in 3-D printing. Since it is relatively efficient, the process requires less energy to manufacture the products, especially in the final assembly. Part consolidation also promotes fewer emissions and long-term fuel economy when it comes to manufacturing cars and airplanes.
More opportunity to recycle and reuse
3-D printing is an additive method, so how does it reuse its waste and unwanted products? The problem lies in human error. Engineers produce prints that have no use or can’t be used. But instead of throwing them, 3-D printing allows reusing the parts. This is possible by separating different materials and shredding the prints to reuse. One example is the OWA filament range produced from old plastic scraps.
When it comes to recycling, 3-D printers can break down single-used plastics, such as water bottles, by transforming them into raw materials. Meanwhile, others incorporate natural materials, such as algae, cellulose, and coffee grounds. Although 3-D printing also produces waste like traditional manufacturing, most of the scraps are recyclable.
The discussion above is just one of the many innovative ways 3-D printing is accelerating sustainability in manufacturing. The growth possibilities are absolutely endless, and there are plenty of opportunities for creativity. While there’s still room for improvement, the industrial sector should now harness its efforts to embrace 3-D printing as an additional tool to the manufacturing process.